Osteoarthritis
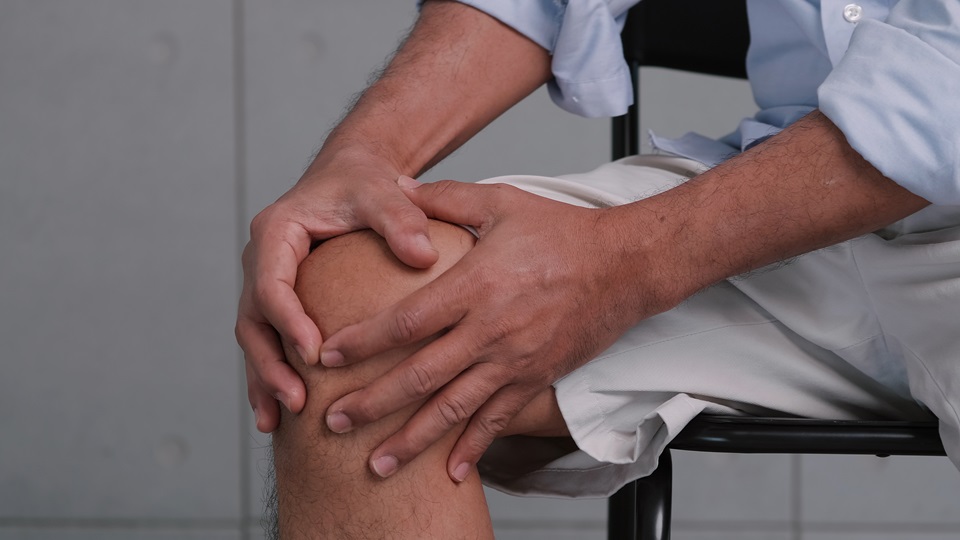
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common joint disease affecting millions of Australians.
Osteoarthritis is a condition that affects the entire joint, including the cartilage, joint lining, ligaments, and bone. When the cartilage, which acts as a cushion on the ends of bones, starts to break down, the bones can rub against each other, leading to swelling, pain, and stiffness. In addition, bony growths can develop around the edge of the joint, causing knobby swelling. It is common for the tissues surrounding the joint to become inflamed as well.
Osteoarthritis commonly affects the knees, hips, fingers, and big toe.
Common Treatment:
The goal of osteoarthritis treatment is to reduce pain and improve function.
Currently, there is no cure for OA, but there are treatments that can effectively control symptoms.
Exercise can reduce joint pain, improve muscle strength, and decrease the chance of disability caused by OA. Weight loss can also be beneficial.
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as Paracetamol and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Joint injections of corticosteroids (also known as cortisone shots) or hyaluronic acid lubricant (Synvisc) can provide months of relief from OA pain. Surgical treatment may be an option for severe cases.
Adaptive devices such as braces, walking sticks, and shoe insoles can help with some of the symptoms.
Working with a physiotherapist or occupational therapist can help learn safe exercises for OA and properly use assistive devices.
