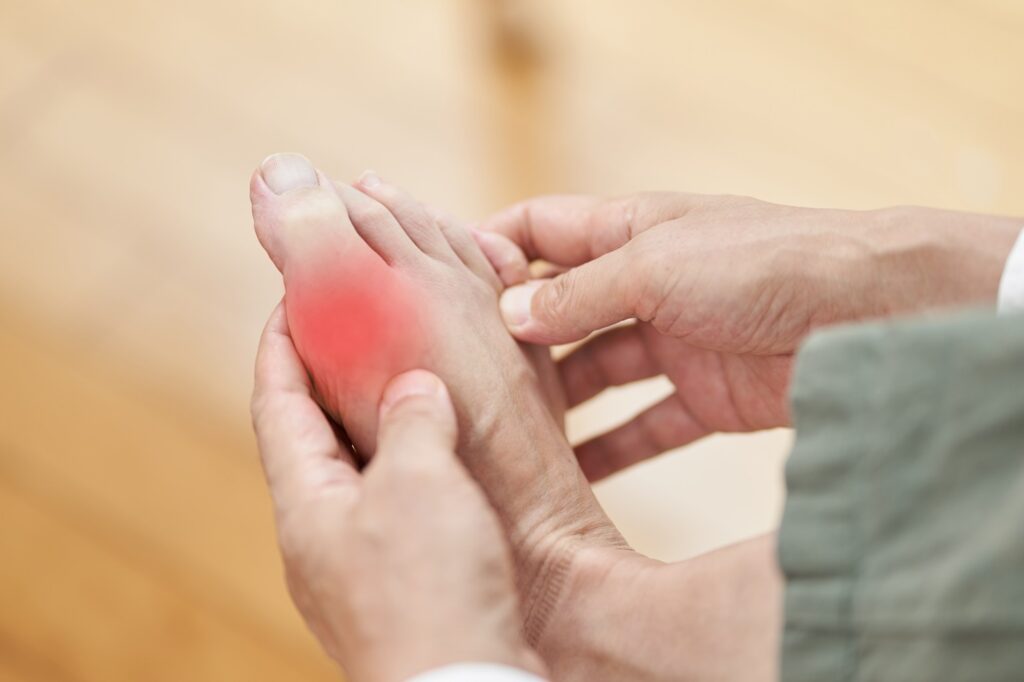
Gout
Gout is a type of arthritis that occurs due to the accumulation of excessive uric acid in the body. It often results in sudden pain and inflammation in a single joint, usually the big toe or other joints in the feet. Uric acid is a natural substance in the blood that is filtered out by the kidneys. However, if the levels become too high or the kidneys are unable to eliminate enough of it, urate crystals may form and settle in a joint, leading to pain, swelling, and redness. Men are more prone to gout than women. A diet high in purines, excessive alcohol consumption, and medications such as diuretics and conditions like dehydration can increase the likelihood of developing gout.
There are several treatments for gout, which can include medications to reduce inflammation, lower uric acid levels in the blood, or aid the kidneys in removing excess uric acid. During an attack, pain and swelling can be alleviated through the use of Colchicine or Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), as well as Glucocorticoid (steroid) pills or injections directly into the joint.
Gout treatment aims to lower uric acid levels to dissolve or prevent crystals. Allopurinol (Xyloprim) and Febuxostat (Adenuric) inhibit uric acid production, while Probenecid helps the kidneys excrete uric acid.
